Hair Transplant Scar – The Good and The Bad
Hair transplants offer a solution for those who want to restore their hairline and regain their confidence. However, one of the main concerns that people have about hair transplants is the potential for an unpleasant appearing hair transplant scar
There are two main types of hair transplants: Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT). While both methods are effective in restoring hair, the main difference is how the follicles to be transplanted are extracted. As a result, they also differ in the type of scarring that they leave behind.
FUT Hair Transplant Scar
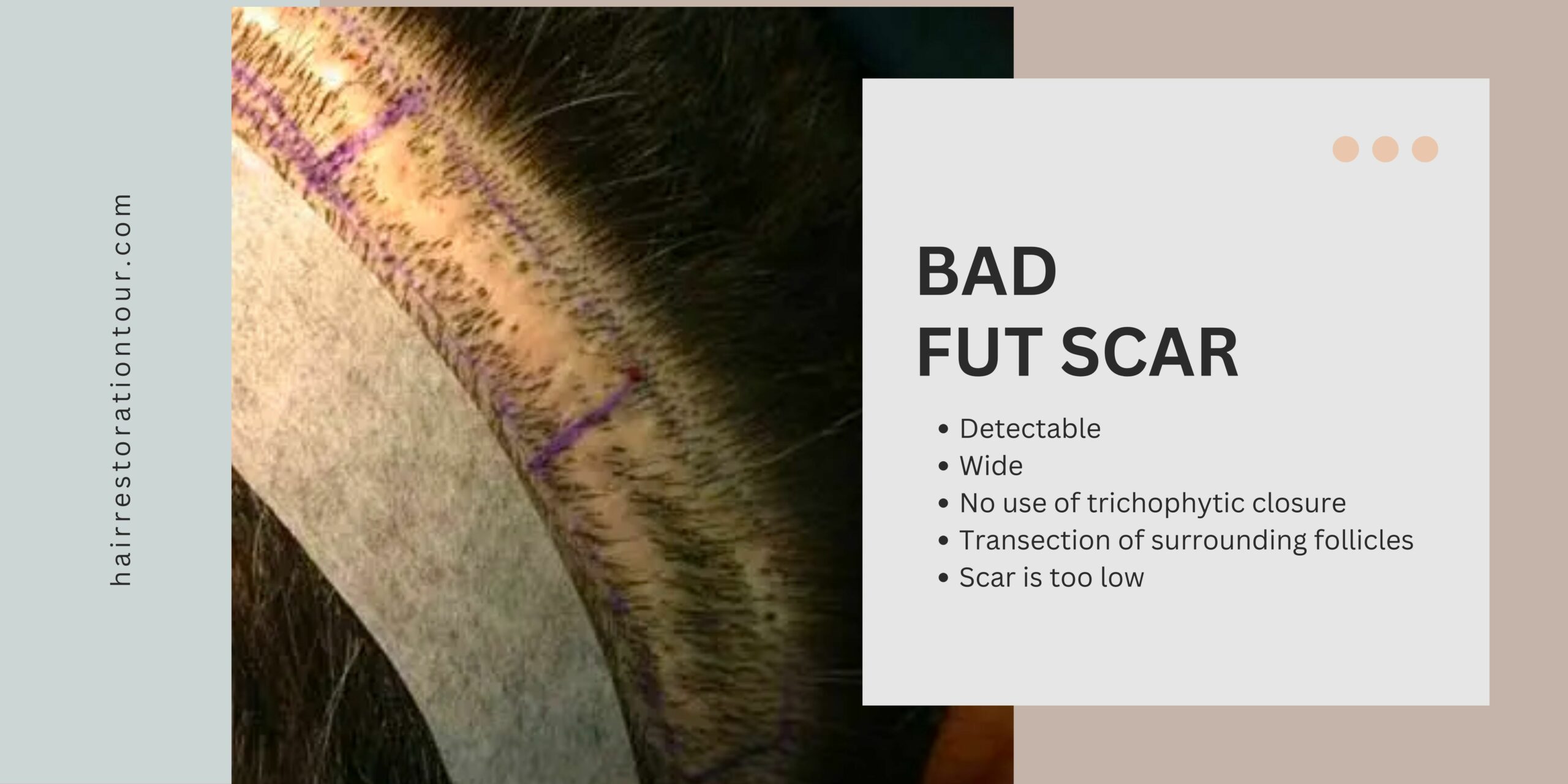
FUT, also known as strip harvesting, involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area (usually the sides and the back of the head) and then dissecting it to isolate the individual hair follicles. The donor area is then sutured closed, leaving a linear scar that can be several inches long. The scar is typically hidden by surrounding hair, but it may be visible if the hair is cut short.
Below, is an example of a good FUT hair transplant scar and a bad hair transplant scar:
Good FUT Scars

Bad FUT Scars
FUE Hair Transplant Scars
On the other hand, FUE involves removing individual hair follicles from the donor area using a small punch tool. At a skilled clinic, the holes left behind are very small, and they typically heal quickly without leaving any visible scarring. However, in some cases, where the harvest may not have been done optimally, FUE can result in tiny white scars that may be visible if the hair is cut very short.
Good FUE Hair Transplant Scars

Bad FUE Hair Transplant Scars

How To Minimize Hair Transplant Scars
It’s important to note that scarring is a natural part of the healing process and cannot be completely avoided. However, with proper care and attention, the appearance of scars can be minimized.
For FUT, the key to minimizing scarring is to choose a skilled and experienced surgeon who can perform the procedure with precision and care. The surgeon should consider the use of advanced techniques to close the incision, such as trichophytic closure, which allows the hair to grow through the scar, making it less visible.
For FUE and FUT, following the post-operative instructions carefully may also influence proper healing. This includes avoiding strenuous activity, wearing loose-fitting hats to avoid rubbing against the donor area, and keeping the scalp clean and dry. Additionally, choosing a skilled and experienced surgeon who uses advanced techniques, can help minimize the risk of scarring.
Hair Transplant Scar Repairs
If you have a visible scar from a previous hair transplant surgery using the FUT technique, scar repair options include:
- Removing the existing scar tissue and then closing the wound with a more advanced surgical technique to minimize scarring
- Transplanting hair into the scar to hide the scar
- A combination of the above two options
If you have visible scars from a previous hair transplant surgery using the FUE technique, options to improve their appearance may include:
- Transplanting hair into the scars to lessen their visual impact.
- Scalp micropigmentation: This is a non-surgical option where tiny dots of pigment are tattooed onto the scalp to mimic the appearance of hair follicles to help camouflage the scar.
Example of FUE Hair Transplant Scars Repair Using SMP

Image courtesy of Chroma Clinic Scalp Micropigmentation
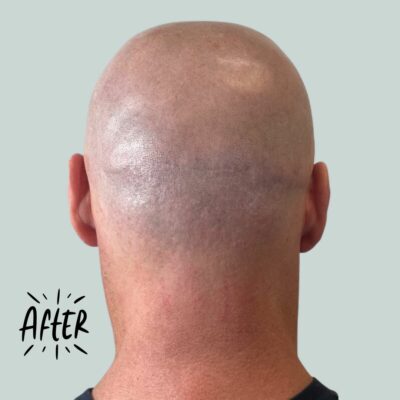
Image courtesy of Chroma Clinic Scalp Micropigmentation
Hair Transplant Scars Summary
In summary, hair transplants are a safe and effective way to restore hair and regain confidence. However, scarring is a potential side effect that should be considered when deciding which method to use. FUE and FUT both have their pros and cons when it comes to scarring, but with proper care and attention, the appearance of scars can be minimized. Choosing a skilled and experienced surgeon who uses advanced techniques is crucial in achieving the best possible outcome.


